Vulva | Definition, Anatomy, & Function
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia, comprised of all the structures located outside the body between the legs. It includes the area around the vaginal opening, the labia majora (outer lips), labia minora (inner lips), the clitoris, the mons pubis (fatty pad above the pubic bone), and the entrance to the urethra.

vulva definition
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia, comprised of all the structures located outside the body between the legs. It includes the area around the vaginal opening, the labia majora (outer lips), labia minora (inner lips), the clitoris, the mons pubis (fatty pad above the pubic bone), and the entrance to the urethra. The vulva can vary significantly in size, shape, and color between individuals and can undergo changes throughout a woman's life, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause. It serves as the entrance to the vagina and is involved in sexual arousal and stimulation.
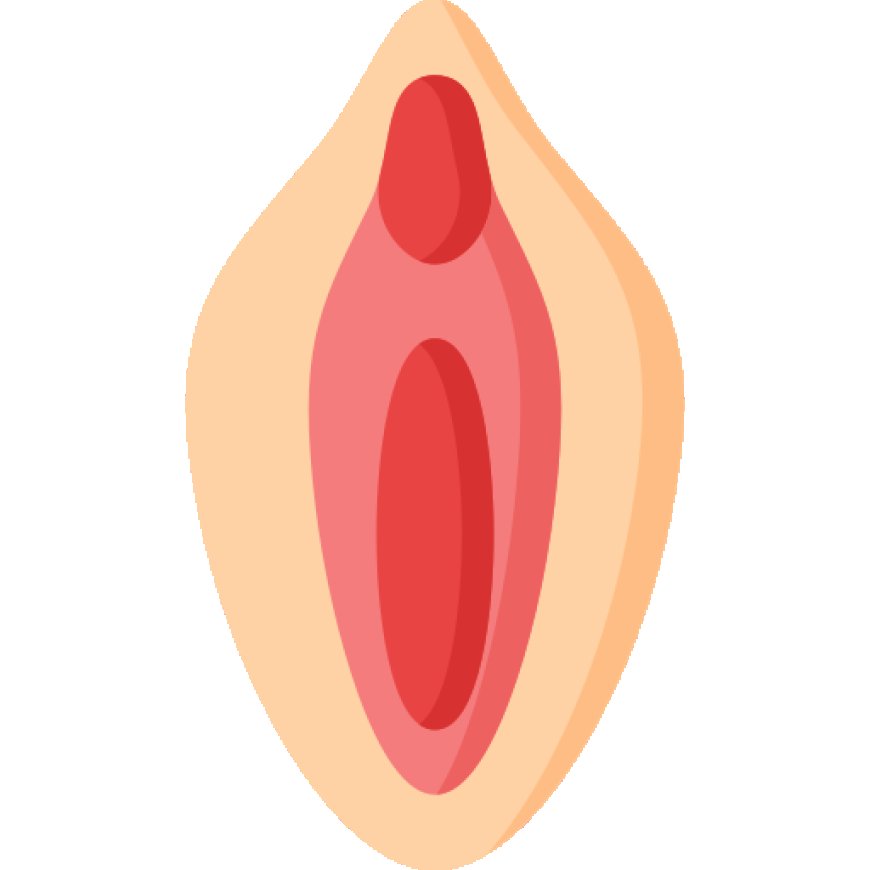
Definition of Vulva in Biology
The vulva or pudendum is the external part of the female reproductive system. The vulva or pudendum, protects the urethra, vestibule, and vagina, women’s reproductive organs.
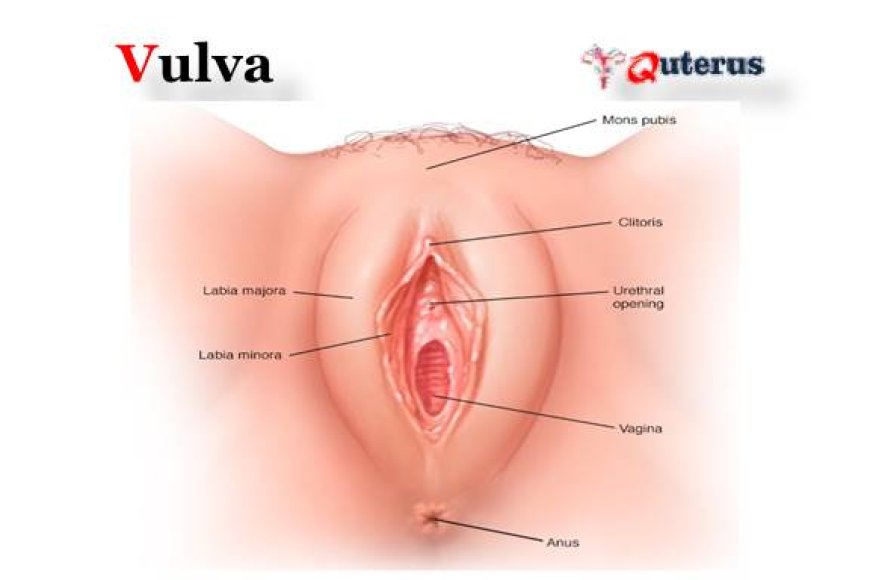
The term ‘vulva’ refers to all the components that make up the female external reproductive organs. The labia majora, mons pubis, labia minora, vestibular bulbs, clitoris, vulva vestibule, Skene’s glands, Bartholin’s glands, vaginal opening and urethra are the components of the vulva.
vulva Anatomy
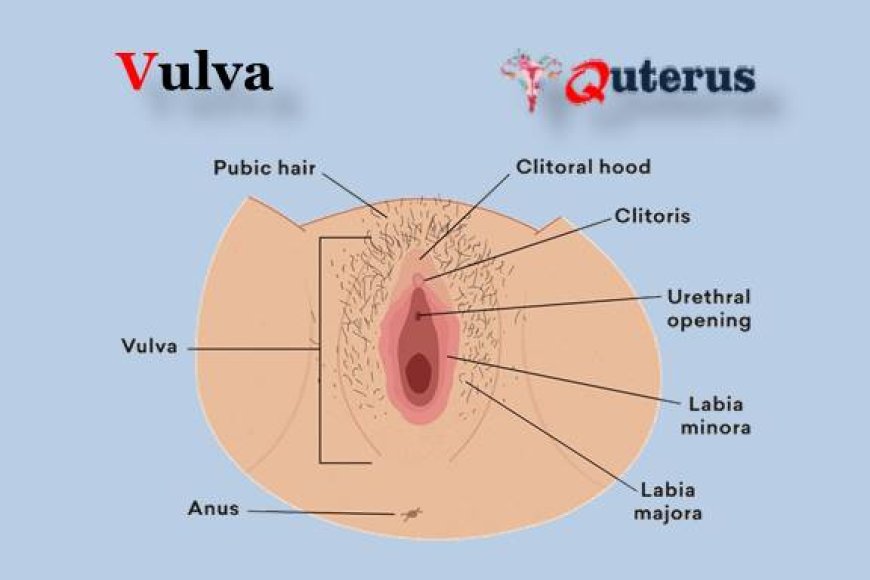
The vulva is the external part of the female genitalia, and it consists of several structures, including :
1.Mons Pubis :
The fatty tissue that is located in the pubic region.
2. Labia majora:
The larger, outer folds of skin that surround the opening of the vagina.
3. Labia minora:
The smaller, inner folds of skin located inside the labia majora. The word "labia majora" is defined as the larger lips. The labia majora are a prominent pair of cutaneous skin folds that will form the lateral longitudinal borders of the vulval clefts. The labia majora forms the folds that cover the labia minora, clitoris, vulva vestibule, vestibular bulbs, Bartholin's glands, Skene's glands, urethra, and the vaginal opening. The anterior part of the labia majora folds comes together to form the anterior labial commissure directly beneath the mons pubis. While the posterior part of the labia majora comes together to form the posterior labial commissure. The labia majora engorges with blood and appears edematous during sexual arousal.
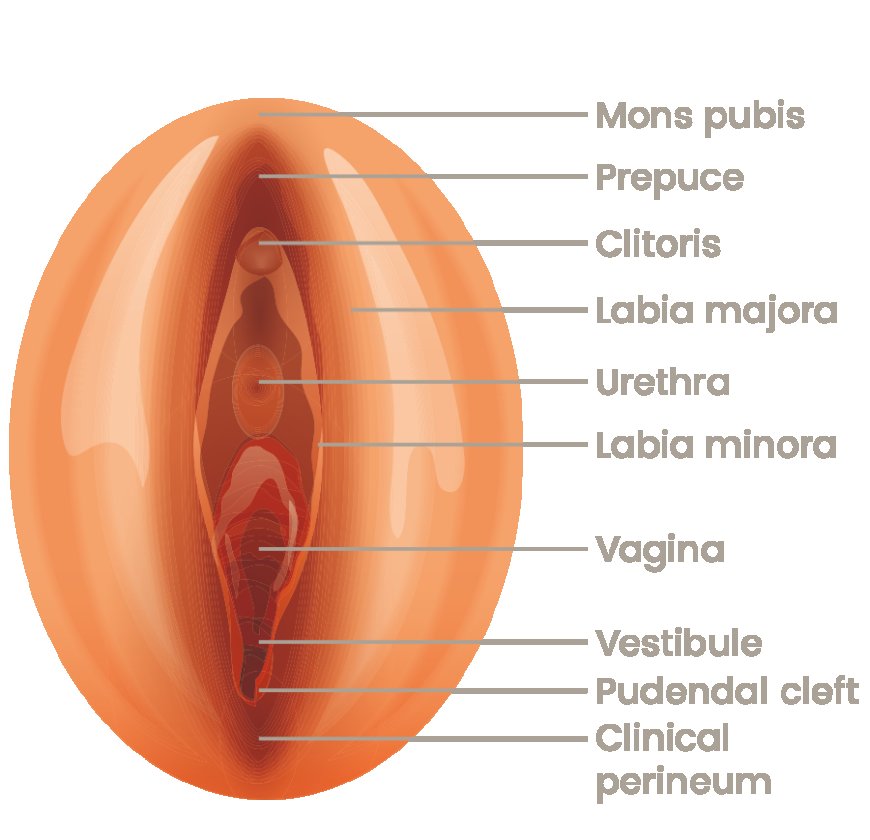
4. Clitoris :
A highly sensitive organ positioned at the top of the vulva that is involved in sexual arousal.
5. Vestibule :
The area of tissue located between the labia minora. The area between the labia minora is the vulva vestibule. This is a smooth surface that begins superiorly just below the clitoris and ends inferiorly at the posterior commissure of the labia minora. The vulva vestibule contains the opening to the urethra and the vaginal opening. The borders of the vulva vestibule are formed from the edge of the labia minora. There is a demarcation between the vulva vestibule and the labia minora called Hart's lines. Hart's lines identify the change from the vulva vestibule to the labia minora. This change of skin appearance is visible by the smoother transitional skin appearance of the vulva vestibule to the vulvar appearance of the labia minora.
6.Vestibular bulbs :
The vestibula r bulbs (homologous to the bulb of the penis in males) are structures formed from corpus spongiosum tissue. This is a type of erectile tissue closely related to the clitoris. The vestibule bulbs are two bulbs of erectile tissue that starts close to the inferior side of the body of the clitoris. The vestibular bulbs then extend towards the urethra and vagina on the medal edge of the crus of the clitoris. Eventually, the vestibular bulbs will split and surround the lateral border of the urethra and vaginal. The vestibular bulbs are believed to function closely with the clitoris. During sexual arousal, the vestibular bulbs will become engorged with blood. The engorgement of blood then exerts pressure onto the corpus cavernosum of the clitoris and the crus of the clitoris. This exertion of pressure onto the clitoris is believed to induce a pleasant sensation during sexual arousal.
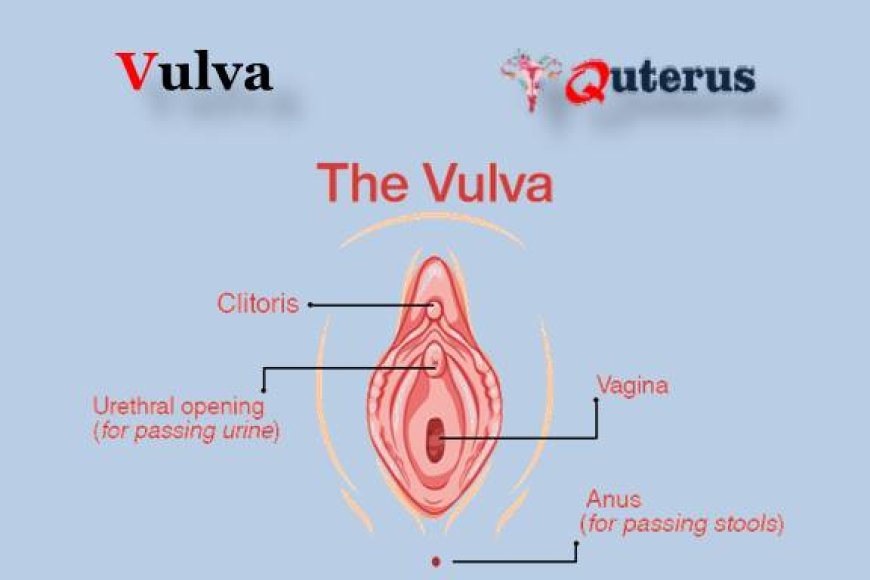
7. Urethral opening :
The external opening to the urethra, which carries urine from the bladder.
7. Vaginal opening :
The entrance to the vagina, which is usually covered by the labia minora. The vagina is an elastic, muscular tube connected to the cervix proximally and extends to the external surface through the vulva vestibule. The distal opening of the vagina is usually partially covered by a membrane called the hymen. The vaginal opening is located posterior to the urethra opening. The function of the vagina is for sexual intercourse and childbirth. During sexual intercourse, the vagina acts as a reservoir for semen to collect before the sperm ascending into the cervix to travel towards the uterus and fallopian tubes. Also, the vagina also acts as an outflow tract for menses.
8.Bartholin's glands :
Two small pea-sized glands located on either side of the vaginal opening that secrete lubrication. The Bartholin's glands also known as the greater vestibular glands (homologous to the bulbourethral glands in males) are two pea-sized glands located slightly lateral and posterior to the vagina opening. These two glands function to secrete a mucus-like substance into the vagina and within the borders of the labia minora. This mucus functions as a lubricant to decrease friction during intercourse and a moisturizer for the vulva.
The anatomy of the vulva can vary significantly between individuals, but these structures are the primary components that make up the external female genitalia.

Learn from the video also the vulva
The Vulva - The Vagina's Neighborhood - 4
Vulva - Learning Objectives
Picture of the vulva
vulva Function
The vulva has multiple functions, including sexual function, protection and elimination.
1.Sexual function :
The vulva plays an essential role in sexual arousal and stimulation. It contains several highly sensitive nerve endings, including those found in the clitoris, which is the primary source of sexual pleasure in women. During sexual stimulation, the blood flow to the vulva increases, causing it to become engorged and lubricated, which prepares the vagina for penetration.
2.Protection :
The vulva also provides protection to the internal genitalia from bacteria, moisture, and other external factors that can cause infection. Its hair and sebaceous glands contribute to this protection by producing a natural lubricant and preventing the growth of unhealthy bacteria.
3.Elimination :
The vulva has an essential role in eliminating waste from the body. The urethra, which carries urine from the bladder, opens to the vulva, as does the vagina and the anus, which carries stool from the rectum.
Overall, the vulva plays a crucial role in several important biological functions and is an essential part of the female reproductive system.

Frequently Asked Questions
What's a vulva on a female?
The vulva is the global term that describes all of the structures that make the female external genitalia. The components of the vulva are the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulva vestibule, Bartholin's glands, Skene's glands, urethra, and vaginal opening.
Does every female have a vulva?
Everyone's vulva looks a little different, but they're all made up of the same basic parts. The labia (lips) are folds of skin around your vaginal opening. The labia majora (outer lips) are usually fleshy and covered with pubic hair. The labia minora (inner lips) are inside your outer lips.
What is my vulva area?
The external female genital area is called the vulva. The outer folds of skin are called the labia majora and the inner folds are called the labia minora.
Where exactly is the vulva?
The vulva is the outer part of the female reproductive system. It's also part of the external genitalia. The vulva includes the mons pubis. This is the rounded area in front of the pubic bones at the lower part of the belly (abdomen).
What is normal vulva size?
They are about 0.4 to 6.4 cm in length, and about 2 cm wide, on average. It is important to note that the actual range is much wider, with normal variants being anywhere from 1.2 to 10 cm in length and 0.7 to 5 cm in width.
What color is a woman's vulva?
Most women's vulva appears to be some shade of red, pink, or burgundy, but this will vary from woman to woman depending on skin tone and other factors. The color will often change over time, such as after puberty, following sexual intercourse, or with arousal.
What is another name for vulva?
synonyms for vulva
On this page you'll find 11 synonyms, antonyms, and words related to vulva, such as: genitalia, gonads, privates, pudenda, private parts, and reproductive organs.
Why is vulva so long?
Genetics: Some people are born with large or differently shaped labia. Hormonal events: The labia may change in size during puberty2 or after childbirth. Aging: Changes over time may lead to labial hypertrophy. Restrictive clothing: Regularly wearing clothing that's tight against the labia can lead to changes
Does vulva change with age?
As the body gets older and estrogen levels decrease, the body loses fat and collagen and the result is that the skin and tissue of the vulva and labia becomes thinner and look less plump. This loss of fullness is completely normal, and the labia may also become smaller and paler due to decreased blood flow to the area.
What is a healthy vulva like?
There's really no such thing as a “normal” looking vulva. Vaginas and vulvas are as unique as faces — they all have the same parts, but everyone's looks a little different. Labia (the inner and outer lips) come in all shapes and sizes. People can have dangly labia, puffy labia, or barely-there labia.
Is vulva smell normal?
All vaginas — including healthy ones — have a mild odor. Your vaginal scent can change in response to sex, menstruation, pregnancy, etc. However, a strong, unpleasant vaginal odor with a discharge may be a sign of a health problem like vaginitis
Which part of vulva is sensitive?
Your entire vulva is an erogenous zone — a part of your body that gets sexually stimulated when touched. Your clitoris is the most sensitive part of your vulva. It's capable of producing the most intense and most pleasurable sexual responses in your body. Your clitoris is sensitive to all types of touch.

We provide you with authentic, trustworthy and revelant information

Have issue with the content?
 Disclaimer
Disclaimer
The information given on our website www.uterusq.com is being posted only for the purpose of knowledge and information, before using them, choose them completely and check the correctness with your subject matter expert. We (www.uterusq.com) have no responsibility for any kind of loss.







